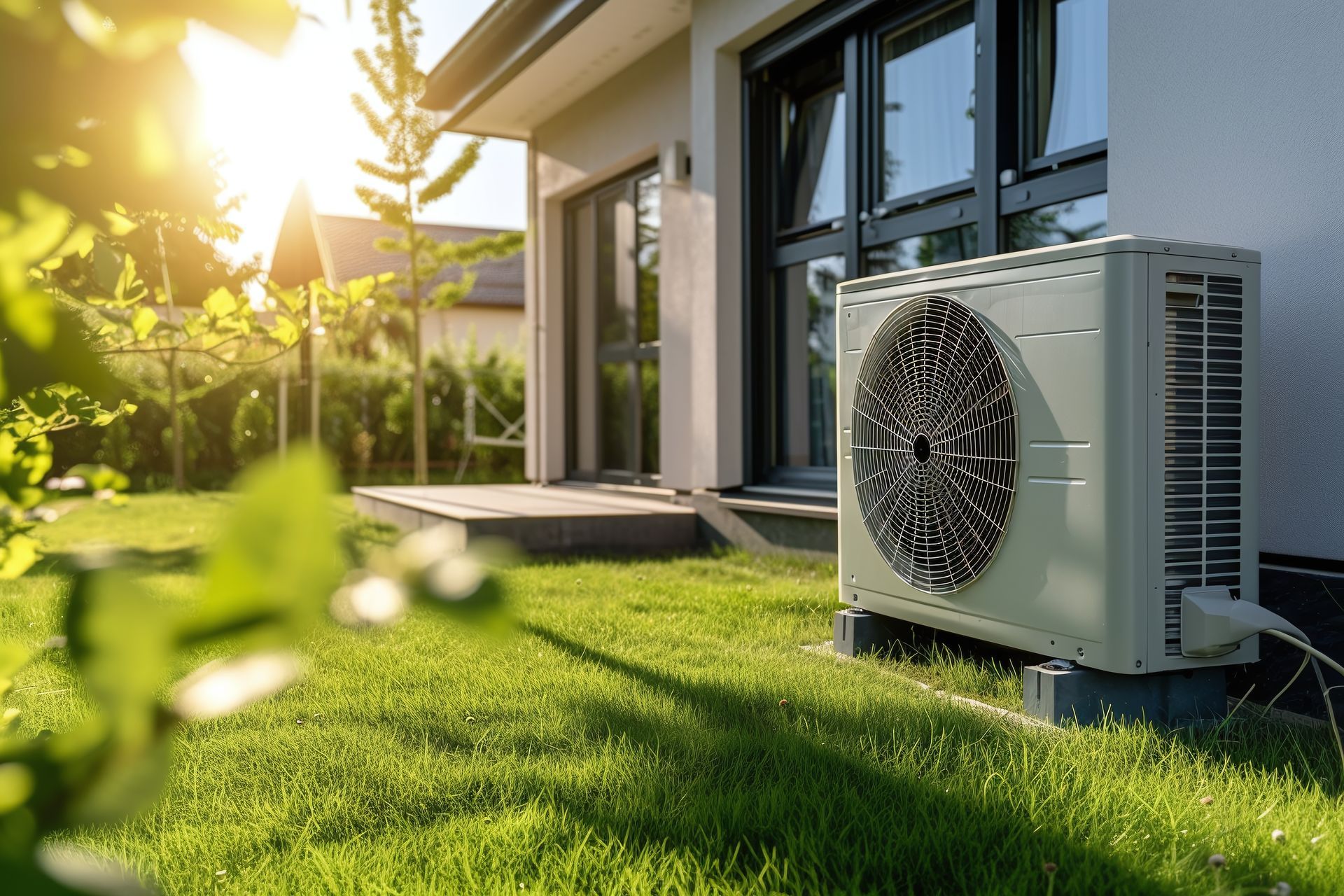
What Is A Heat Pump
What is a Heat Pump System & How Does It Work?

A heat pump is a relatively recent feature that can be added to or comes built into an air conditioner. It essentially reverses the direction of heat exchange. When the air conditioner is operating, it pulls heat out of the air inside and transfers that heat outside via the condenser coils. By activating the heat pump, it reverses the direction of heat exchange so that heat is pulled from outside and directed inside. These are electric powered, so they are more ecofriendly than a furnace which usually operates by burning some kind of natural gas. While they do provide an alternative to having a gas burning furnace, they do have some limitations that still require other sources of heat for colder temperatures.
How Does a Heat Pump Heat & Cool?
Heat pumps effectively collect and redistribute heat from the air or the ground. They use the same method of cooling that air conditioners utilize to move heat from one location to another, but in reverse. The heat pump will collect heat from outside and then manipulate thermodynamics with refrigerants to transfer that heat inside. Each heat pump system is on a closed loop system of refrigerants that get circulated through the compressor and the air handler. After the heat has passed through the system via the refrigerants, it will get released inside. When it is time to cool a space, the system can be reversed by activating the reversing valve which changes the direction of the refrigerant flow.
Pros & Cons of Heat Pumps
Using a heat pump has unique features and downfalls which make it a perfect supplement to an existing heating system.
Pros of Heat Pumps
- Cost less to operate
- General maintenance and upkeep is completed with AC maintenance
- No unsafe byproducts
- More ecofriendly
- Operates quietly
- One system provides heating and cooling
- Longer lifespan
- Reduced reliance on natural gas
Cons of Heat Pumps
- Limited function if extremely cold outside
- Installation can be pricey
- Installation can be complex with an interior and exterior component
- Heat is not as powerful as traditional heaters
Air Conditioner vs Heat Pump
Heat pumps and air conditioners are 2 sides of the same coin. They operate using the same principles, and within the same system. The primary difference is which direction the flow of heat is turned to. Air conditioners will extract heat from the inside and blow that heat outside. Heat pumps will extract heat from outside and redirect that heat inside while blowing cold air outside. Having a heat pump included in your air conditioning system could potentially eliminate the need for a supplementary heating system in warmer climates. Otherwise, it is recommended that a traditional furnace is used to offset time where colder exterior temperatures prevent the heat pump from operating efficiently.
Furnace vs Heat Pump
The primary difference between these 2 heating systems is how they generate heat. A heat pump does not create heat, it just concentrates it and moves it from one location to another. A furnace usually creates heat by burning a fuel like natural gas or oil. This results in the heat pump being much more energy efficient in addition to not producing harmful byproducts like carbon emissions and carbon monoxide. In most situations where extremely cold temperatures are not likely to occur, a heat pump should be sufficient to warm a home. That said, a furnace does beat out heat pumps in performance as they can produce heat in all situations including when it is cold outside. The lifespan of both a furnace and an AC unit with a heat pump are both close to 15-20 years with proper general maintenance.
What Types of Heat Pumps Exist?
There are several types of heat pumps that are primarily differentiated by where they draw heat from.
Ducted Air Source Heat Pumps
Ducted air source heat pumps come with traditional HVAC systems that use a central AC unit that is connected to an exterior unit that helps disperse heat. This system utilizes ductwork and vents to pass air throughout a home by pushing air to each room equally.
Ductless Air Source Heat Pumps
Split ductless air source heat pumps uses an exterior unit that is connected to individual room AC units that are mounted high up to help regulate temperature. They operate much like ducted systems but instead have refrigerant running to each room rather than a central AC unit. This helps each room maintain an independent temperature range. The pricing of a ductless system increases with the number of AC units are attached to the exterior unit.
Geothermal Heat Pumps
Geothermal heat pumps draw heat from the ground. These systems use a buried pipe system to extract geothermal energy from the ground. These are generally more functional for large properties that have space for lots of underground piping. With the larger setup comes much higher installation costs.
What Are the Primary Components in a Heat Pump System?
The components that make up a heat pump system are the same that you would find in an AC unit. They include:
- Exterior unit that can act as a condenser and evaporator when cooling and heating
- Indoor handler that contains the coils that help condense and relocate the heat
- Motor that drives the fan
- Refrigerant used to transfer heat
- Compressor that helps regulate refrigerant pressure
- Reversing valve to activate heat pump
- Expansion valve to help control directional flow of refrigerant
What to Know Before You Buy a Heat Pump System
There are several considerations that users will have to take into account when determining if a heat pump is an appropriate heating option.
Heat Pump Energy Efficiency
Energy efficiency is rated on 4 key elements:
- SEER (Seasonal Energy Efficient Ratio): This measures the cooling efficiency of air source heat pump systems. The federal minimum standard is between 13 - 14 SEER depending on where your home is.
- HSPF (Heating Seasonal Performance Factor): This measures the heating efficiency of air source heat pump systems. The federal minimum standard for all units is 7.7 HSFP.
- EER (Energy Efficiency Ratio): This measures the cooling efficiency of geothermal heat pump systems. The federal minimum standards are 17.1 - 21.1.
- COP (Coefficient of Performance): This measures the heating efficiency of geothermal heat pump systems. The federal minimum standards are 3.1 – 4.1.
These measures are important to know when selecting heat pump / AC options for your home’s climate. Warmer climates will need a higher SEER while colder climates will want a higher HSFP. The higher efficiency heat pumps will have a 20+ SEER and an 8.5+ HSPF. Generally, the higher the rating, the more expensive a unit will be, so keep that in mind when selecting a potential heat pump system.
Where Do Heat Pumps Work Best?
Heat pumps work the best in climates that are moderate where temperatures stay comfortably above freezing. Because these systems rely on existing heat to transfer inside, colder climates that frequently drop below freezing make these systems less useful. In places with lower temperatures, ground source heat pumps make more sense due to consistent geothermal temperatures. It also makes sense to supplement a heat pump with a traditional furnace in places that get extremely cold.
Features to Look for in a Heat Pump
There are several bonus features that will help improve a heat pumps efficiency.
- 2 Speed compressors: Allows heat pumps to work more efficiently at close to capacity
- Zone control systems: Use dampers to help regulate temperature at different rates in different rooms
- Variable / 2 speed motors: Helps regulate the speed of airflow through an AC unit to keep noise down and efficiency up
- Desuperheater: Recovers wasted heat and uses it to heat water in the system
- Scroll compressor: Helps compress the refrigerant which help increase heat output compared to piston compressors
- Hybrid systems: Integrates traditional heating into the system to offset times when colder temperatures make it difficult to cycle heat inside
- Demand defrost control: Helps minimize frost buildup with a unit designed to help prevent exterior frost buildup
Heat Pump Sizing
Getting the sizing of your heat pump system right is critical to ensuring that your home can get the heat it needs. If the heat pump system is not sized properly, it will either produce too much or too little heat. If the heat pump is not strong enough, it will remain on while it continues to try and heat the space. If the heat pump is too strong, it will cycle on and off frequently which will reduce the overall longevity of the heat pump system. A licensed HVAC technician at GS Home Services will be able to help find the right unit for you. We take into account the home’s current insulation, windows, and current system to ensure we provide the best recommendation possible.
Heat Pump Maintenance
General maintenance is recommended for your AC unit, so it makes sense that it would apply to your heat pump system. Being sure to check that components are clean and operating properly will help ensure that the heat pump lasts for a long time. Without the right upkeep, a heat pump system can easily become dirty or damaged which will end up shortening the life span of the unit. It is important to check the filters and replace them when needed, clean and dust the unit to prevent buildup, and check for damages, leaks, or any other issues that might cause heat pump failure. A licensed HVAC technician can help with some of the more technical checks like monitoring refrigerant charge and flow, addressing any temperature problems, checking noises that indicate mechanical problems, etc.
How to Improve Heat Pump Efficiency
There are only a few things that can be done to improve a heat pump’s efficiency, but there are several things that can be done to ensure that the heat pump doesn’t have to work as hard.
- Insulate walls and attic
- Seal doors and windows with weather stripping
- Seal & insulate ductwork
- Set smart thermostats to adjust temperatures as needed when people are around
Contact GS Home Service to Inquire About Heat Pumps
Heat pumps can be a great addition to a home that helps reduce the reliance on gas burning furnaces. If you have been considering using a heat pump as your primary or supplementary heating system, call today to talk to a licensed representative. We can find the best option for you to ensure that you are provided with an energy efficient heat pump unit.